In today’s energy-dependent world, battery systems play a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted power supply for various applications, from data centers to renewable energy storage. Extending the lifespan of these battery systems is not only cost-effective but also essential for maintaining optimal performance. Here are some key strategies to help you get the most out of your battery systems.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Routine Inspections:
Regularly inspect batteries for signs of physical damage, swelling, or leakage. Look for corrosion on terminals and connectors, as this can impede performance and lead to failures. Establish a maintenance schedule that includes cleaning, tightening of connections, and testing the electrical performance of the battery systems.
Performance Monitoring:
Utilize a BMS to continuously monitor critical parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge (SoC). A BMS can alert you to potential issues before they become serious problems. Regularly analyze performance data to identify trends and anomalies. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, such as balancing cells or adjusting operating conditions.
Optimal Charging Practices
Proper Charging:
Adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications for charging rates and cycles. Incorrect charging can cause overheating, excessive gassing, and reduced capacity. Use intelligent chargers that can adjust the charging process based on the battery’s condition and ambient temperature. This helps in maintaining optimal charge levels without overcharging.
Temperature Control:
Charge batteries within the recommended temperature range, typically 20-25°C (68-77°F). Charging at higher temperatures can accelerate aging, while low temperatures can lead to incomplete charging. Implement active cooling or heating systems to maintain a stable temperature during charging and discharging cycles, especially in environments with significant temperature fluctuations.
Environmental Conditions
Temperature Management:
Batteries perform best in a stable climate. High temperatures accelerate chemical reactions, leading to faster degradation, while low temperatures reduce the battery’s ability to deliver power. Use air conditioning or heating systems to maintain the battery storage area within the optimal temperature range. Insulation can also help mitigate temperature extremes.
Humidity Control:
Excessive humidity can lead to condensation and corrosion of battery components. Keep the storage area dry and use dehumidifiers if necessary. Ensure proper ventilation to avoid the buildup of gases, particularly for lead-acid batteries that can emit hydrogen gas during charging.
Balanced Usage
Avoid Overloading:
Properly assess the power needs and ensure the battery system is not overloaded. Consistently operating at or near maximum capacity can strain the batteries. Distribute the electrical load evenly across multiple batteries or battery banks. This helps in preventing any single battery from being overburdened, which can lead to uneven wear and tear.
Regular Cycling:
For batteries designed for cyclic use, such as those in renewable energy systems, ensure they are regularly charged and discharged. This prevents capacity fade and maintains their efficiency. Do not leave batteries in a fully discharged state for extended periods, as this can lead to sulfation in lead-acid batteries and deep discharge damage in lithium-ion batteries.
Use High-Quality Components
Invest in batteries and components from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and reliability. High-quality batteries have better materials and construction, leading to longer lifespans. Ensure that all components within the battery system, such as chargers, inverters, and connectors, are compatible and designed to work together. Incompatible components can cause inefficiencies and potential damage.
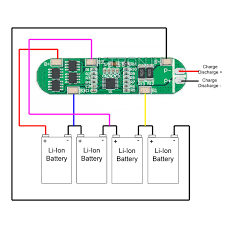
Implement a Battery Management System (BMS)
A BMS provides real-time data on various parameters, allowing you to monitor the health and performance of each cell. This helps in early detection of issues such as cell imbalance or thermal runaway. The BMS can automatically balance the charge across cells, ensuring uniform performance and preventing weaker cells from degrading faster.
Regularly Update Firmware and Software
Keep the firmware and software of your BMS and other related systems up to date. Manufacturers often release updates that improve performance, add new features, and enhance safety. Regular updates also include security patches that protect your battery management system from vulnerabilities, ensuring reliable and secure operation.
Conclusion
Extending the lifespan of your battery systems requires a combination of regular maintenance, optimal charging practices, environmental control, balanced usage, and the use of high-quality components. By implementing these strategies, you can ensure that your batteries perform efficiently and reliably over the long term, providing you with the best return on your investment.