The downstream of lead is mainly lead-acid batteries, which basically determines the overall demand for lead. Lead-acid batteries can be divided into four categories according to specific uses: starting batteries, power batteries, backup power supplies and energy storage batteries. Among them, starting batteries are the most important use of lead-acid batteries. In this article, we mainly analyze the future development prospects of lead-acid batteries from the four major fields of automobile and motorcycle starting batteries, electric vehicle power batteries, energy storage batteries, and 5G communication power supplies.
Automobile and motorcycle starting battery field
In recent years, although lithium-ion batteries have been widely used in the field of new energy vehicles, lead-acid batteries are still almost irreplaceable in the field of starting cars and motorcycles, because the development of other batteries has not yet fully reached the use environment of starting batteries. requirements, the main reasons are as follows:
Cost requirements: The cost of lead-acid batteries is lower than other batteries, and there is no need to change the charging power system, and the later maintenance costs are lower.
Performance requirements: The starting battery is required to be able to start the vehicle normally at -40°C, while other batteries have poor cold start performance and are difficult to meet the power usage requirements of people in cold winter areas.
Safety requirements: The starting battery is generally located near the engine in the cabin, in a high temperature and enclosed space. Other batteries are prone to overflow toxic gases when impacted.
Therefore, the starting field, as an inherent field of lead-acid batteries, has incomparable advantages. Affected by energy conservation and emission reduction policies, the installation rate of start-stop systems in new cars is expected to further increase in the future. As of the end of 2023, according to estimates by market data analysis agency Hedges Company, the current global car ownership is approximately 1.446 billion vehicles. The market size is expected to grow to US$27.336 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 14.5%.
Electric vehicle power battery field
The power batteries of conventional electric vehicles mainly rely on lead-acid batteries that have a history of hundreds of years. Especially in two-wheeled electric vehicles, lead-acid batteries are still the mainstay.
It is currently the battery with the highest market share for two-wheelers and has the advantages of being cheap, safe and reliable.
As a mature battery technology, lead-acid batteries have experienced two to three hundred years of testing. Its pollution is controllable and will not be eliminated. It is an indispensable part of the secondary rechargeable battery field. Research shows that most of the sources of lead pollution in the atmosphere come from vehicle exhaust and aviation fuel, with less than 1% coming from lead-acid batteries.
In addition, as a recyclable metal, lead has a recovery rate of up to 98%, which can supplement the shortage of raw materials and effectively reduce the problem of rising raw material prices due to raw material consumption. Therefore, based on the above factors, if electric vehicles are to be industrialized, they must start at low speed. To achieve marketization, the first choice is to use lead-acid batteries. Lead-acid batteries are indispensable and important elements on the road to the industrialization of electric vehicles, from technical stability to cost scalability.
Energy storage battery field
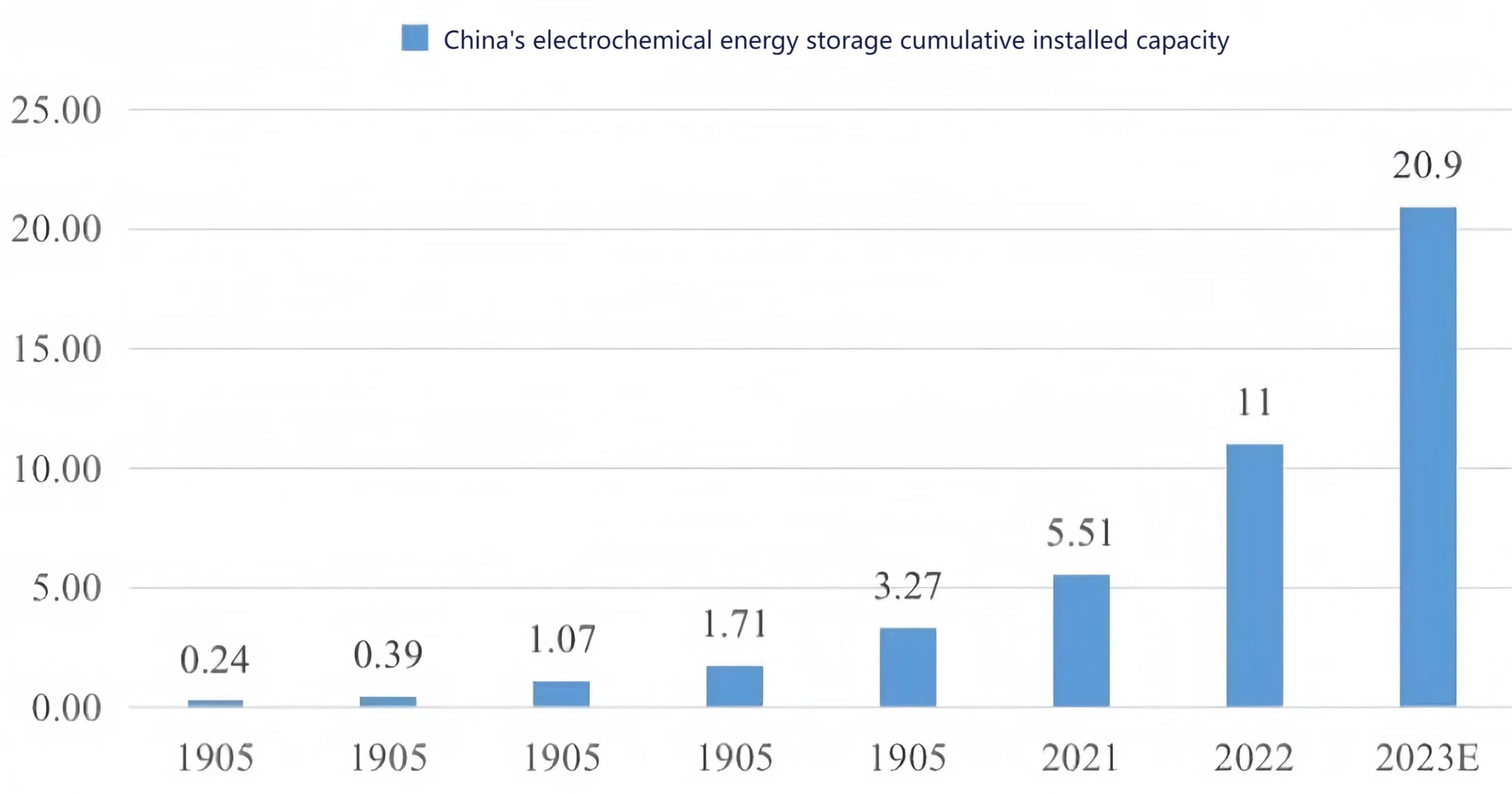
In recent years, the energy storage industry has entered a period of rapid development. According to incomplete statistics from CNESA’s global energy storage project database, as of the end of 2022, the cumulative installed capacity of power energy storage projects in operation in China is 59.8GW, accounting for 25% of the total global market, with an annual growth rate of 38%, and an annual growth rate of power scale. reached 128%, and the annual growth rate of energy scale reached 141%.
Among new types of energy storage, lithium-ion batteries occupy an absolutely dominant position, accounting for 97%. This is due to the continued cost reduction of lithium-ion batteries, high energy density, long life, and no memory effect. Lead-acid batteries only account for 3.1%, but due to their high safety and other advantages, the market for lead-acid batteries is still developing in many microgrid projects. From a comprehensive perspective such as environmental adaptability and cost, it is more competitive than lithium batteries.
However, in recent years, with the advancement of compressed air energy storage, flow batteries, sodium-ion batteries, flywheels and other battery technologies, if lead-acid batteries are to continue to develop in the energy storage industry, they need to increase scientific research and development based on the characteristics of the use occasions. In order to reduce costs, increase life and improve PSOC performance.
5G communication power supply field
Generally, the service life of domestic communication base station batteries is 5 years. If a base station is equipped with two sets of 48V400Ah lead-acid batteries, the demand for each base station is 38.4Kvah. According to the research institute’s calculations, the demand for lead-acid batteries for new base stations in the communications field will decrease year by year. However, not all existing lead-acid batteries have been retired, and it will take at least 5-8 years to completely replace lead-acid batteries with lithium iron phosphate batteries.
Overall, in addition to the field of starting batteries, lead-acid batteries are facing the risk of being replaced in all other fields. In order to effectively cope with the competition from new energy sources such as lithium batteries and sodium batteries, lead-acid batteries urgently need technological revolution in terms of lightweight, long life, low cost, fast charging and PSOC performance. In the future, lead-acid battery technology must draw on advanced technologies and concepts from other disciplines such as materials science, electronic technology, network technology, etc., and apply them for its own use, in order to have a place in the increasingly fierce competition in the future.