With the surge in the popularity of artificial intelligence, a recent study delves into the implications of the rising electricity consumption demands necessitated by the technology’s rapid expansion.
The remarkable surge in artificial intelligence (AI) during the 2020s will likely be a significant milestone for decades. The advent of AI has fundamentally reshaped how humans engage with learning, problem-solving, art, communication, and many everyday activities.
The Growth of AI
The birth of traditional AI as we know it‒early approaches that primarily used symbolic and rule-based systems to simulate human intelligence‒was sometime in the 1950s. While AI has a long history, the present rapid growth of this industry is attributed to generative AI. Generative AI employs machine learning algorithms to generate outputs derived from a training data set.
Programs like ChatGPT, Dall-E, and Midjourney have been rapidly consumed in the last year, marking the most significant technological advancement since social media. Since January 2023, ChatGPT has over 100 million monthly users, making it more popular than Instagram or TikTok.
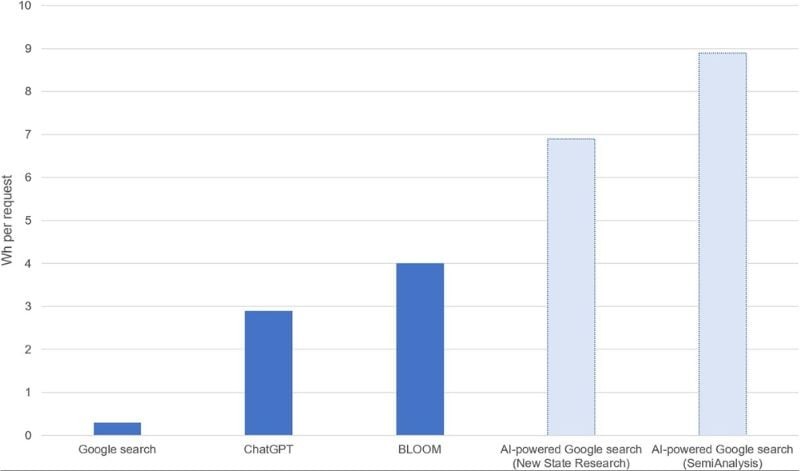
Estimates of energy use by AI-powered web searches, based on a 2023 study.
AI Energy Consumption
The swift integration of AI into our daily lives is creating a potential challenge alongside the global push for sustainable energy practices. The energy demand of the AI industry is only growing with its rapid adoption, and these figures raise significant concerns.
While data center electricity usage from 2010-2018 increased only by about 6 percent, there is growing concern that the computational resources required to develop and maintain AI models could significantly elevate data centers’ contribution to global electricity consumption. In 2022, it was estimated that global data center electricity consumption ‒240-340 TWh ‒ accounted for about 1.3 percent of global electricity demand.
Global AI-related consumption alone could reach 134 TWh by 2027. That is comparable to the annual consumption rates of countries like Argentina, the Netherlands, and Sweden. Looking at more specific incidents of AI growth.
Google‒already a prominent AI advocate‒was to incorporate technology similar to ChatGPT into its daily 9 billion searches. This alone would result in an annual energy consumption of 29.2 TWh, equivalent to the entire electricity usage of Ireland.
Ultimately, the energy needs within the AI industry are bound to grow as these technologies become increasingly widespread. Asking AI companies to offset the electricity consumption of their data centers with renewable energy would be a logical first step in directly addressing this issue. For more industry information, please always pay attention to our official website.